Resources
This page contains some key resources on walking and cycling, including an archive of the documents produced by the Australian Bicycle Council.
| Date Added | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 |
Gender Sensitive Urban Design Implementation Toolkit ACT Government The Gender Sensitive Urban Design (GSUD) Toolkit is a comprehensive resource designed to provide designers with essential principles, practices, and strategies for creating inclusive public spaces. With a particular focus on the needs of women, girls, gender diverse individuals, and other vulnerable people, the toolkit offers a range of strategies to address the multifaceted aspects of gender sensitivity in the public realm.
|
01/03/2024 | View |
 |
Active Travel Plan and Design Guide ACT Government This Plan outlines ACT Government priorities for strengthening active travel and improving quality of life. Projects included throughout demonstrate what these priorities mean in practice. |
01/03/2024 | View |
 |
Planning and designing for active transport Department of Transport Western Australia Collaborating with and guiding state and local government and industry partners to plan, design and develop active transport solutions to help make it an easy choice for people of all ages and abilities to walk, wheel and ride. |
02/02/2024 | View |
 |
Australian Transport Assessment and Planning (ATAP) Mode Specific Guidance: M4 Active Travel Australian Transport Assessment and Planning (ATAP) At a glance:
|
13/11/2023 | View |
 |
Promotion, encouragement and behaviour change Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland On this page: |
27/10/2023 | View |
 |
Universal access Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland On this page: |
27/10/2023 | View |
 |
Speed management and integrated treatments Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland On this page: |
27/10/2023 | View |
 |
Road crossings Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland On this page: |
27/10/2023 | View |
 |
Paths for walking Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland On this page |
27/10/2023 | View |
 |
Construction and maintenance Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland On this page: |
27/10/2023 | View |
 |
Shade and street trees Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland On this page: |
27/10/2023 | View |
 |
Pedestrian and Walking Guidance: Supporting facilities Department of transport and Main Roads, Queensland On this page: |
27/10/2023 | View |
 |
Urban planning and urban design Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland On this page: |
27/10/2023 | View |
 |
Walking Network Planning Guidance Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland More people will walk when everyday destinations are connected by comfortable, direct, safe and accessible routes. Walking network plans (WNPs) are a first step to creating better places to walk. The Queensland Government is committed to achieving the Queensland Walking Strategy 2019–2029 vision of walking becoming 'an easy choice for everyone, every day'. When we talk about walking, we also include running and moving with the help of a mobility device (such as a wheelchair, mobility cane or a walking frame). The following guidance supports practitioners to prepare WNPs and a prioritised works program to make the plan a reality. |
13/10/2023 | View |
 |
Pedestrian Demand Forecasting Guideline Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland The intent of this document is to provide guidance to practitioners to forecast demand for pedestrians
|
17/07/2023 | View |
 |
Getting to and from public transport Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Getting to and from public transport is integral to every public transport journey. All passengers must make their way to a public transport stop to board public transport, then make their way from where they disembark to their final destination. Often referred to as the ‘first and last mile’, the actual length of these trips can range from less than 100m to many kilometres. First and last mile connections are critical to a viable and enjoyable public transport journey experience. Key issues relating to the quality and ease of access to and from a public transport stop include:
It is important that those involved in public transport planning consider the whole of the passengers' journey. When planning for public transport journeys, the following questions should be considered:
|
19/05/2023 | View |
 |
Accessibility Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Key design parameters for accessibility such as kerb arrangements, access ramps, tactile ground surface indicators, and pedestrian movement. |
19/05/2023 | View |
 |
40 km/h speed limits in high volume pedestrian areas Transport for NSW A guide to identifying and implementing 40 km/h speed limits in high volume pedestrian areas. |
15/05/2023 | View |
 |
Bike-friendly business Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland Bike riders are customers who choose to arrive by bike. There’s a big opportunity for businesses to achieve growth by becoming bike-friendly. More than ever, bike riders want to go from A to Business. There’s growing demand to stop, shop and spend at bike-friendly businesses of all different types, from local cafes right through to tourism destinations. Being bike-friendly can be a point of difference for a business. It means the business can offer more customers more choice and freedom. |
06/04/2023 | View |
 |
Speed management guide: Road to Zero Edition Waka Kotahi NZTA The Speed management guide: Road to Zero edition supports regional transport committees, regional councils and road controlling authorities |
12/08/2022 | View |
 |
Queensland Guide to Traffic Management Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland The Queensland Guide to Traffic Management (QGTM) is issued under the authority of Section 166 of the Transport Operations (Road Use Management) Act 1995. The contents of QGTM are issued as 'approved notices' under Section 166(2) of said Act. The Department of Transport and Main Roads has adopted Austroads' Guide to Traffic Management (AGTM) 2020 as part of national harmonisation. As a result, the QGTM will only provide requirements and recommendations specific to Queensland and has precedence over the equivalent Austroads Part. |
08/07/2022 | View |
 |
Programme/project logic models Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency The links provide different guides to developing programme/project logic models. |
07/04/2022 | View |
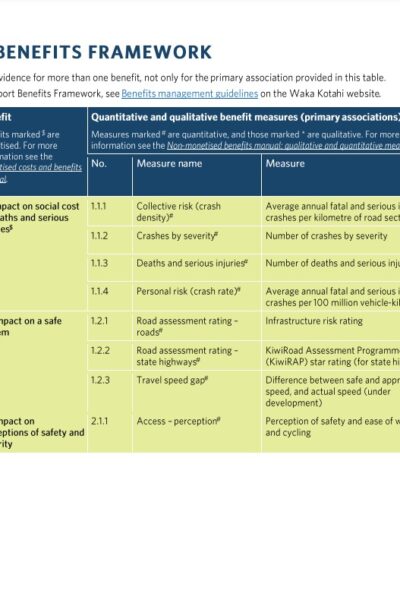 |
Benefits management guidance Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency This guidance is to help transport planners, business case writers and anyone involved in transport investment understand the Land Transport Benefits Framework and how to use benefits management in their work. |
07/04/2022 | View |
 |
Tactical Urbanism Handbook Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency The draft Tactical Urbanism Handbook has been developed as a tool to help councils and communities deliver tactical urbanism projects to a high standard, using a collaborative best-practice approach. |
07/04/2022 | View |
 |
How to Talk About Urban Mobility and Transport Shift: A Short Guide, 2020 The Workshop This guide is designed for technical experts, communicators and advocates working to deliver urban mobility solutions that grow the share of travel by public transport, walking and cycling. Its purpose is to help us use more effective strategies to: improve people’s understanding, based on best evidence, of why a shift in transport modalities away from cars and towards active and public transport is needed; help people designing and leading the shift to have better conversations with the public; motivate people to act in support of these shifts. This guide is based on a literature review conducted by The Workshop on behalf of Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency. |
07/04/2022 | View |
 |
Tactile Indicator Installation Note Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency The purpose of this technical note is to provide some high-level recommended practice to contractors carrying out the installation of tactile pavers as requested in an industry survey in 2018. This is a supplementary publication aimed at roading and utility contractors to provide a simple guide for reinstating tactile pavers affected by their works. |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
RTS14 Guidelines for facilities for blind and vision impaired pedestrians Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency RTS 14 is the official guide that ensures that design and operation of roads and paths caters for blind and vision impaired pedestrians. It also takes into account the needs of people with impaired mobility. It provides detailed requirements for a continuous accessible path, tactile ground surface indicators and audible tactile traffic signal features. |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
Bridging the Gap: NZTA Urban Design Guidelines Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency The guidelines seek to improve the understanding of what good urban design means in a transport project. The guidelines are intended for consultants, contractors, project managers, stakeholders and the community who participate in the planning, design, construction and maintenance of our transport networks. They are also intended for other Transport Agency staff whose work and actions affect urban design outcomes. |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
Pedestrian Planning and Design Guide Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency The Pedestrian planning and design guide is New Zealand's comprehensive official guide to planning and design for walking. It sets out ways to improve New Zealand’s walking environment |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
Low-powered Vehicles Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency There is a range of low-powered devices that New Zealanders use for travel or recreation. While these vehicles and devices offer the benefit of increased mobility, they can also increase your safety risks on and around the road. |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
Designing a Cycling Facility Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Provides users with best practice guidance, either directly or through links to appropriate sources for all stages of design, from concept stage through to detailed design |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
Planning a Cycling Network Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Provides users with best practice guidance, either directly or through links to appropriate sources for all stages of planning a cycle network |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
Technical note #4: Buffered Cycle Lane Design Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Guidance on the design of buffered cycle lanes for varying carriageway widths |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
Technical note #2: Separated Cycleways at Side Roads and Driveways Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency This updated guidance covers how to design a priority-controlled cycle crossing of a side road or driveway |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
Buffered Advance Stop Box Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Provides a treatment solution for advance stop boxes to improve visibility of cyclists from heavy vehicles and decrease the level of vehicle encroachment |
19/10/2021 | View |
 |
Access Control Devices Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Guidance on the design, installation and management of access control devices on facilities where cyclists are permitted to be present. |
18/10/2021 | View |
 |
Considering Historic Heritage in Walking and Cycling Projects Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency The draft Handbook for tactical urbanism has been developed as a tool to help councils and communities deliver tactical urbanism projects to a high standard, using a collaborative best-practice approach. |
07/10/2021 | View |
 |
Draft Handbook for Tactical Urbanism in Aotearoa Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency The draft Handbook for tactical urbanism has been developed as a tool to help councils and communities deliver tactical urbanism projects to a high standard, using a collaborative best-practice approach. |
06/10/2021 | View |
 |
Shared and Separated Path Guidelines Department of Transport WA This document provides practitioners with guidance surrounding the planning and design of shared and separated paths in Western Australia to enable the safe and efficient movement of bicycle riders of all ages and abilities. It is intended to be a convenient and practical reference guide aimed at practitioners with varying levels of experience. |
06/10/2021 | View |
 |
Draft Handbook for tactical urbanism in Aotearoa - Guidance: roadway art Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency A supplement to the Handbook for tactical urbanism provides draft guidance on compliant application of using road artwork effectively and safely in New Zealand. |
30/09/2021 | View |
 |
High-use driveway treatment for cycle paths and shared paths Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Provides a treatment solution for commercial and high-use access points on cycleways and shared paths. |
30/09/2021 | View |
 |
Cycle Parking Planning and Design Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency This guidance summarises best practice provision of parking and end-of-trip facilities for people who cycle. |
30/09/2021 | View |
 |
Signs and markings to designate paths for pedestrians and cyclists Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Guidance on where and how to use markings and/or signs that designate paths for pedestrians and/or cyclists. |
30/09/2021 | View |
 |
Sharrow Markings Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Guidance on the implementation of shared lane markings (‘sharrows’). |
30/09/2021 | View |
 |
Design Guidance for Pedestrian and Cycle Rail Crossings Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency and KiwiRail have been leading the development of a design guide for pedestrian and cycleway treatment at level crossings. The guide will improve safety, usability, compliance, consistency and will simplify the design process. |
21/09/2021 | View |
 |
Cycling Network Guidance Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Cycling network guidance – planning and design (CNG) framework aims to promote a consistent, best-practice approach to cycling network and route planning throughout New Zealand. |
06/09/2021 | View |
 |
Urban Cycleways Programme: National monitoring and data reporting requirements Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Outlines the national monitoring and reporting requirements for the Urban Cycleways Programme (UCP) projects. Includes best practice methodologies for measuring the success of new cycle infrastructure as well as wider network monitoring. |
18/08/2021 | View |
 |
Monitoring and Reporting Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency A description of the monitoring required, particularly once the implementation of the cycle network plan has started. |
18/08/2021 | View |
 |
Cycling Standards and Guidance Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Cycling network guidance – planning and design (CNG) framework aims to promote a consistent, best-practice approach to cycling network and route planning throughout New Zealand. |
18/08/2021 | View |
 |
Workplace Cycling Guide Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency This online guide provides all the key information to help your workplace better provide for people on bikes. |
18/08/2021 | View |
 |
Employer e-bike Purchase Support Schemes Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency Employer e-bike purchase support schemes are helping many more people to purchase e-bikes by addressing the key barrier of the upfront cost. They work through employers negotiating a discount from an e-bike supplier and then providing a wage advance or loan to staff, paid back through salary deductions over a set period. |
13/08/2021 | View |
 |
Cycle Safety Waka Kotahi NZ Transport Agency A few simple tips to stay safe when sharing the road. |
12/08/2021 | View |
 |
Walking and Cycling Program Guidelines Transport for NSW These guidelines outline the priority weighting system that will be used to assess walking and cycling proposals submitted to the NSW Government for funding. |
03/08/2021 | View |
 |
Transport for NSW Economic Parameter Values Transport for NSW This document recommends economic parameter values for common benefits and costs in transport economic appraisals. By providing best-practice approaches and economic parameter values, this document supports the consistent application of cost-benefit analysis (CBA) across the NSW Transport cluster. |
15/07/2021 | View |
 |
Economic Parameter Values Transport for NSW This spreadheet provides all tables in the Transport for NSW Economic Parameter Values. |
15/07/2021 | View |
 |
Cycling and Public Transport Adelaide Metro Information on bikes and the public transport network. |
14/07/2021 | View |
 |
Bike User Guide Department of Transport and Main Roads, Queensland Riding a bike is part of Queensland life. With a few tips and a bit of advice, it’s easy to get rolling. |
09/07/2021 | View |
 |
Walking Space Guide Transport for NSW The Walking Space Guide (Guide) provides a set of standards and tools to assist those responsible for Walking Spaces on streets, to ensure that sufficient space is provided to achieve comfortable environments which encourage people to walk. The Guide offers a clear, consistent set of standards and processes to be applied in designing, planning and implementing the amount of space to be provided according to the intensity of use. It is intended that designs are appropriate to the number of people using footpaths. This guide contains the method for carrying out a Walking Space assessment and offers guidance on how to understand the results. The guide includes an accompanying spreadsheet for recording data and calculating results. |
17/05/2021 | View |
